Intersection of COVID-19 and Alzheimer’s Disease: Genetic Insights and Neuropathological Consequences
Ranjith Balakrishnan 1, Rajasekaran Subbarayan 1,3*, Rupendra Shrestha 2*, Ankush Chauhan 3
Publications: Biochemical Genetics. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s10528-025-11208-x
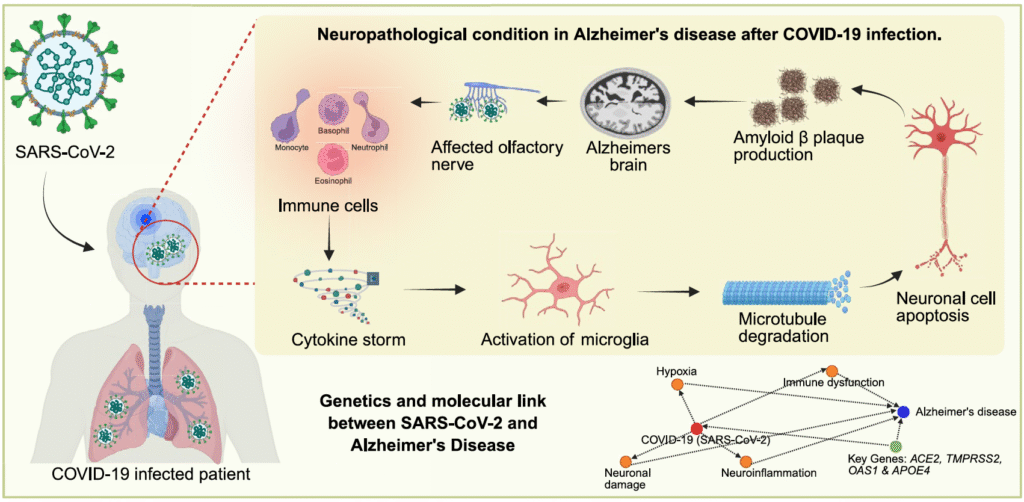
Abstract – The potential link between viral infections and the onset of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has been debated for several years. The emergence of the SARS–CoV-2 pandemic has raised concerns regarding its potential role in predisposing individuals to AD or aggravating its progression. The widespread transmission of SARS–CoV-2 has introduced novel aspects to AD research, driving comprehensive investigations into the possible correlation between COVID-19 and neuropathological manifestations observed in patients with AD. This review explores the complex connection between COVID-19 and Alzheimer’s disease by examining both the direct effects of SARS–CoV-2 on the brain and the indirect impacts of the infection on the overall health of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. An overview of COVID-19 is provided, followed by a detailed discussion of Alzheimer’s disease, including its clinical presentation and neuropathological consequences. Moreover, our review aimed to identify key candidate genes, such as ACE2, TMPRSS2, OAS1, and APOE4, which have been implicated in COVID-19 and AD. We analyzed data from multiple genomic and transcriptomic databases to elucidate the genetic factors underlying the association between these two conditions. Furthermore, with advancements in contemporary genomic technologies, this review highlights potential genetic mutations and variations that may serve as crucial biomarkers, risk predictors, and therapeutic targets. Elucidating these molecular interactions could offer critical insights for advancing future research and formulating innovative therapeutic interventions for Alzheimer’s disease within the framework of SARS–CoV-2 infection.
Cite: Balakrishnan, R., Subbarayan, R., Shrestha, R., Chauhan, A. Intersection of COVID-19 and Alzheimer’s Disease: Genetic Insights and Neuropathological Consequences. Biochemical Genetics. 2025. PMID: 40720045