Circulating miR-542-3p as a Prognostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ranjith Balakrishnan 1, Rajasekaran Subbarayan 1,2*, Maheshkumar Kuppusamy 3, Rupendra Shrestha 4*, Arunkumar Radhakrishnan 5, Ankush Chauhan 2
- Centre for Advanced Biotherapeutics and Regenerative Medicine, Faculty of Research, Chettinad Hospital and Research Institute, Chettinad Academy of Research and Education, Kelambakkam, Tamil Nadu, India.
- Centre for Herbal Pharmacology and Environmental Sustainability, Chettinad Hospital
and Research Institute, Chettinad Academy of Research and Education, Kelambakkam, Tamil Nadu, India. - Department of Physiology & Biochemistry, Government Yoga and Naturopathy Medical College and Hospital, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
- Department of Natural and Applied Sciences, Nexus Institute of Research and Innovation (NIRI), Lalitpur, Nepal.
- Department of Pharmacology, Chettinad Hospital and Research Institute, Chettinad
Academy of Research and Education, Kelambakkam, Tamil Nadu, India.
Publications: Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2025;29(14):e70748 doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70748
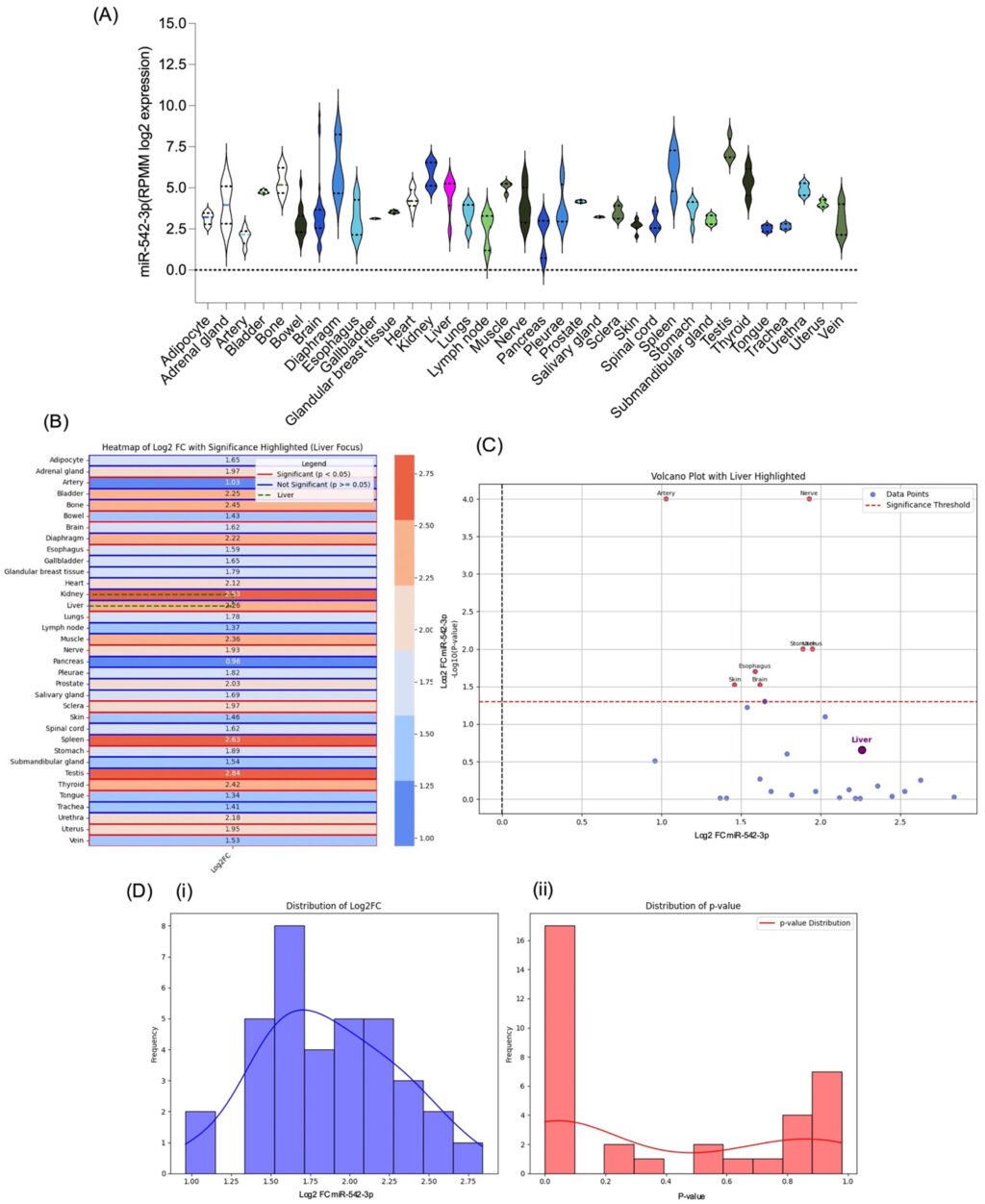
Abstract – Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, particularly in Asia. Despite therapeutic advancements, the prognosis of HCC remains poor. MicroRNAs have emerged as potential biomarkers for HCC prognosis and therapeutic response. This systematic review and meta-analysis examined the association between circulating miR-542-3p levels and HCC progression. Seven studies on HCC and miR-542-3p were selected for the meta-analysis. miR-542-3p showed significant diagnostic potential for HCC prognosis and therapeutic evaluation. Two independent researchers performed data extraction and used the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2) method to assess the quality and risk of bias of the included studies. After the meta-analysis, human miRNA pattern analysis was conducted using the miRBase database, and the expression of miR-542-3p was confirmed based on the results obtained from the human miRNA profile in the tissue atlas database. miR-542-3p has been shown to have significant diagnostic potential for HCC prognosis and therapeutic evaluation. The pooled sensitivity was 0.79 (95% CI, 0.75–0.83), while the pooled specificity was 0.34 (95% CI, 0.29–0.40). The diagnostic odds ratio was 7.2, with an AUC of 0.806, indicating moderate diagnostic accuracy. Network analysis in miRBase links miR-542-3p to liver function, and its location on the X chromosome allows its expression in both sexes, making it widely applicable for the diagnosis of HCC. Thus, miR-542-3p has potential as a prognostic biomarker for HCC, with prospects for integration into therapeutic strategies. Future studies should explore the combination of this with targeted therapies to improve patient outcomes.
Cite: , , , , , and Circulating miR-542-3p as a Prognostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2025;29(14): e70748. PMID: 40717227