Liposome-Encapsulated Melatonin Mitigates Amoxicillin-Induced Neurotoxicity in a Zebrafish
Ranjith Balakrishnan 1, Rajasekaran Subbarayan 1,2*, Rupendra Shrestha 3*, Dhasarathdev Srinivasan 1, Reena Shrestha 4, Ankush Chauhan 2, Dinesh Murugan Girija 5
Publications: Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2025;29(22):e70969. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70969
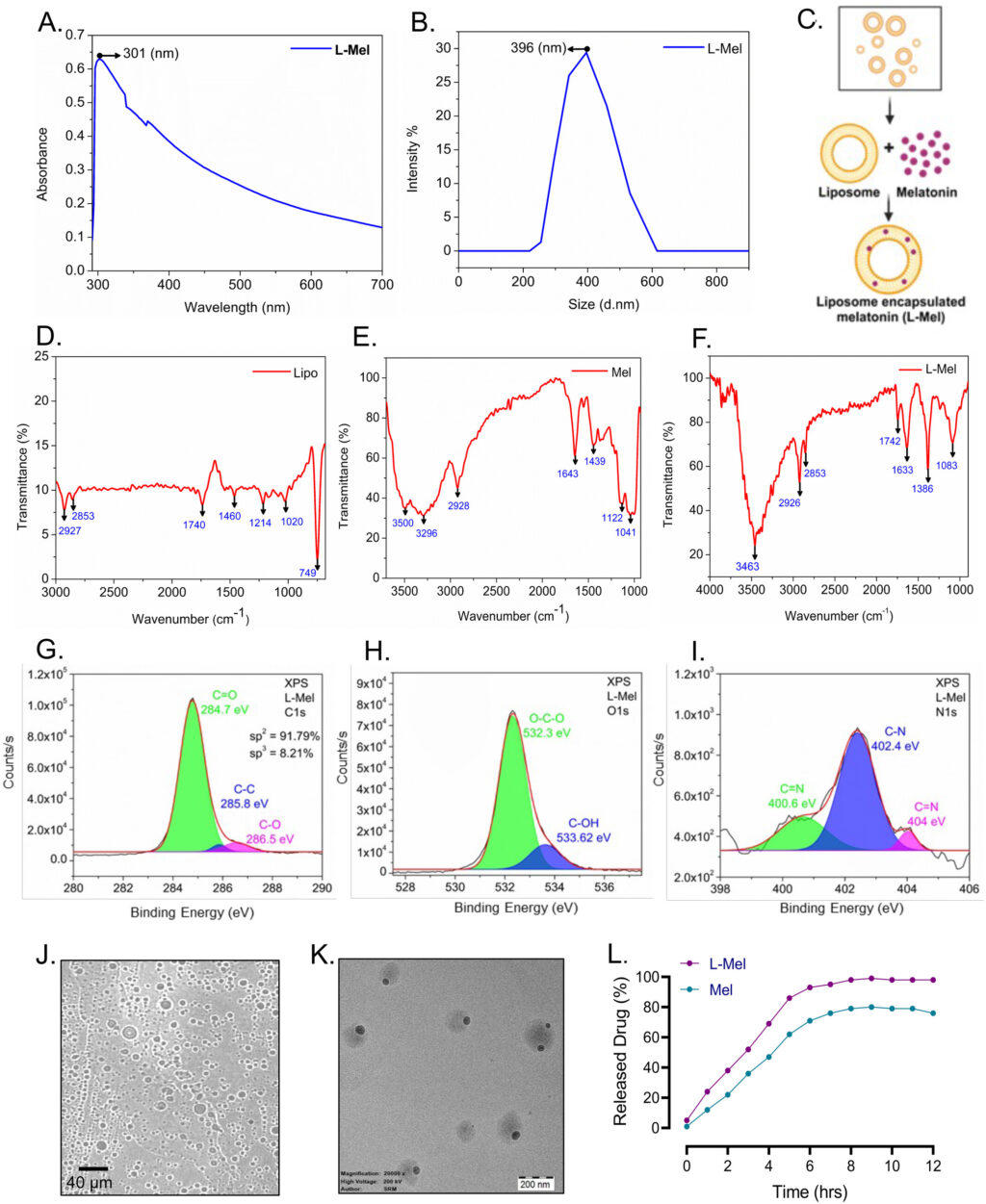
Abstract – Amoxicillin (Amx), a β-Lactam antibiotic frequently used to treat bacterial infections, has been linked to neurological effects, including anxiety, hyperactivity, ambiguity, seizures, and behavioural changes. We examined the neurotoxic effects of Amx in zebrafish and investigated the potential of liposome-encapsulated melatonin (L-Mel) as a therapeutic intervention. Computational studies have indicated that Amx and Mel interact with GABA receptors, suggesting the potential of L-Mel in mitigating Amx-induced neurological changes. Our findings demonstrated that the nanoformulated L-Mel showed reduced toxicity in zebrafish larvae. Administration of L-Mel to Amx-affected zebrafish brain tissue significantly lowered the levels of reactive oxygen species, antioxidants (catalase, superoxide dismutase, and nitric oxide), and proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and NF-kB), based on the fixed EC-50. Behavioural assessments revealed that L-Mel treatment notably enhanced the immobility time and swimming performance, improving the movement abilities of zebrafish with Amx-induced neuroinflammation. Moreover, the GABA/glutamate levels in the neural tissues exhibited significant recovery in the L-Mel group. Gene and protein analysis showed substantial increases in BDNF, CREBBP, ASCL, NF-κB and GABA-A R γ2 in L-Mel treated subjects. Histopathological evaluation revealed that L-Mel treatment markedly attenuated Amx-induced neurotoxicity, as evidenced by reduced neuronal degeneration and necrosis in the brain tissue, indicating a pronounced neuroprotective effect. In conclusion, our research suggests that L-Mel is a promising therapeutic agent for mitigating Amx-induced neurotoxicity.
, , , Liposome-Encapsulated Melatonin Mitigates Amoxicillin-Induced Neurotoxicity in a Zebrafish. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2025;29(22):e70969